
When this doesn’t happen, physicians at Tampa General Hospital will often treat atrial flutter using catheter ablation, which involves using radiofrequency energy to restore a normal heart rhythm. In some cases, atrial flutter will resolve on its own without the need for treatment. If there’s still a question as to what is causing a patient’s symptoms, a physician may direct him or her to undergo an electrophysiological study or wear an event monitor for a certain amount of time. Physicians often use electrocardiograms (EKGs) to diagnose atrial flutter.
#Atrial flutter atrial fibrillation symptoms professional#
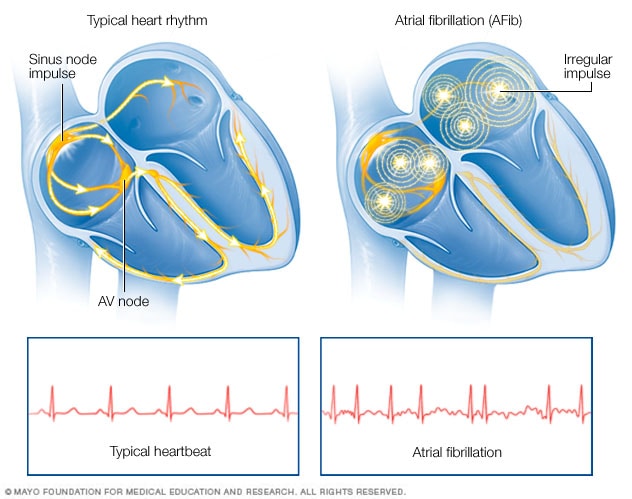
If you think that you might have atrial flutter, it’s important to seek professional medical advice, since this condition can lead to cardiomyopathy and increase your risk of stroke if left untreated. Heart palpitations (a fluttering sensation within the chest).Having previously undergone cardiac surgeryĪlthough atrial flutter doesn’t always produce noticeable symptoms, many individuals with this condition experience:.Having previously undergone catheter ablation to treat atrial fibrillation.There are various risk factors that can increase the chances of developing atrial flutter, including: Sometimes a person may have episodes of both atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation. People with atrial flutter have a heart rhythm that's more organized and less chaotic than that of atrial fibrillation. Many individuals have both of these conditions. Atrial flutter is similar to atrial fibrillation, a common disorder that causes the heart to beat in irregular patterns. But with atrial flutter, the atria beat regularly-they simply beat faster than the ventricles. With atrial fibrillation, the atria beat is irregular. Many people use the terms atrial flutter and atrial fibrillation (AFib) interchangeably, believing that they’re the same condition. But with atrial flutter, problems with the heart’s electrical system cause the atria to beat faster and more frequently than the ventricles. Normally, the heart’s atria (upper chambers) and ventricles (lower chambers) work together to pump blood to the rest of the body-first the atria contract and force blood into the ventricles, and then the ventricles contract and force blood out of the heart. Less commonly, atrial activation can be in a clockwise fashion, and thus electrocardiographic appearance is different, one is unable to differentiate it easily from not isthmus-dependent atrial flutter.Ĭopyright © 2023, StatPearls Publishing LLC.Atrial flutter is a type of abnormal heartbeat, or arrhythmia. The atypical atrial flutter is independent of the CTI, and the origin of the arrhythmia can be in the right atrium or the left atrium.

Typical atrial flutter is seen in the electrocardiogram as continuous negative modulation in inferior leads (II, III, and AVF) and flat atrial deflections in leads I and aVL this is due to the way of propagation and activation of the macro-reentrant circuit as will be described in the pathophysiology section. Typical or cavotricuspid isthmus (CTI) dependent is the most common type of atrial flutter this rhythm originates in the right atrium at the level of the tricuspid valve annulus. Electrical axis of the flutter waves can help to determine the origin of the atrial flutter. Electrocardiographic findings of atrial flutter are flutter waves without an isoelectric line in between QRS complex.

In this review will summarize the management of atrial flutter.Ītrial flutter is one of the most common arrhythmias and is characterized by an abnormal cardiac rhythm that is fast with an atrial rate of 300beats/min and a ventricular rate that can be fixed or be variable that can cause palpitations, fatigue, syncope, and embolic phenomenon.Ītrial flutter is a macro-reentrant tachycardia and depending on the site of origin can be typical or atypical atrial flutter. Atrial fibrillation and atrial flutter are the most common of these atrial arrhythmias, and the other less common supraventricular arrhythmias are atrial tachycardias, atrioventricular reentrant tachycardia, atrioventricular nodal tachycardia, and others. Supraventricular arrhythmias are a diverse group of atrial arrhythmias.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
